Getting started with RHADS
Why Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite?
Organizations face a critical challenge: accelerating development with AI while securing against rising software supply chain threats. Despite open-source components comprising 90% of modern applications, malicious packages increased 156% year-on-year, causing an estimated $60 billion in damages in 2025. This environment demands an integrated platform engineering solution like Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite (RHADS) to balance speed and security.
RHADS combines platform engineering tools with enhanced security capabilities to help accelerate and simplify application development with new enhancements to speed the adoption of AI:
-
Modular design allows it to be integrated with existing platforms and systems including Red Hat’s platforms
-
Integrates with existing security capabilities found in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security
-
Complements existing developer tools from Red Hat including OpenShift Dev Spaces
-
Built on leading open source projects like Backstage and Sigstore
Architecture Overview
RHADS is not just a set of tools; it’s purpose-built for balancing speed and security, integrating into existing workflows. It combines platform engineering tools with enhanced security capabilities to accelerate and simplify application development.
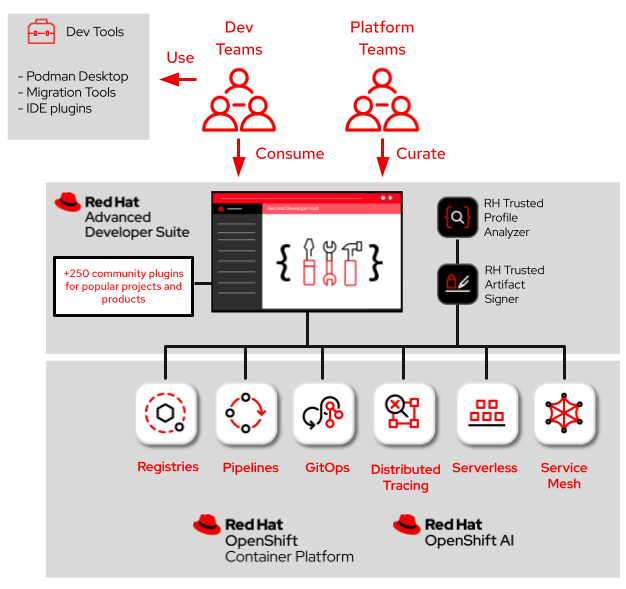
The main components of RHADS are:
-
Red Hat Developer Hub (RHDH): An enterprise-grade, self-managed, and customizable internal developer portal built on Backstage.io. It acts as a central portal for templates, documentation, and tools, reducing cognitive load and setup time. It streamlines development workflows with automated software templates and self-service capabilities. RHDH’s plugin architecture allows for customized software templates and integrates with various tools and services.
-
Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer (RHTAS): Provides a secure, transparent, and fully auditable signing and verification system. It ensures the integrity, authenticity, and provenance of software artifacts throughout the development and deployment lifecycle. RHTAS supports both keyless and key-based signing, simplifies signing using existing user identity (GitHub, Google, SSO), and maintains an immutable audit trail. It’s an enterprise-ready deployment of the Sigstore project. RHTAS also extends its signing and verification capabilities to AI models, improving security during the AI model development lifecycle.
-
Red Hat Trusted Profile Analyzer (RHTPA): Provides platform engineers, developers, and security teams with visibility and actionable insights into the risk profile (vulnerabilities, licenses) of their software supply chain across the entire SDLC. It leverages Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) management, open-source dependency risk analysis, and license tracking to detect vulnerabilities, malicious code, and compliance risks.
RHADS is enhanced by several free, complementary developer tools:
-
Podman Desktop: This free, open-source tool provides a GUI for local container and Kubernetes management, helping developers build, run, and deploy applications on their desktop and reducing "works on my machine" issues. It supports air-gapped installation and includes an AI Lab extension for AI experimentation. While a community project, it receives Cooperative Community Support for Red Hat customers, including those on ARO and ROSA.
-
Red Hat Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA): This toolkit aids in modernizing legacy Java applications for container and cloud-native platforms, enabling assessment, refactoring, and migration with minimal disruption. It accelerates replatforming to OpenShift and will feature future AI integration with Developer Lightspeed for code generation to speed modernization based on static analysis.
-
Red Hat IDE Plugins: These plugins facilitate local coding by integrating Red Hat ecosystem technologies directly into popular Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), and connect IDEs to OpenShift clusters for direct access to resources.
These tools extend the OpenShift experience to developer desktops and complement RHADS’s features for increased productivity and security across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
RHADS complements OpenShift:
-
It extends OpenShift’s capabilities "to the left of the SDLC".
-
It integrates seamlessly with various supported tools and offerings, including OpenShift Dev Spaces, OpenShift Pipelines, and OpenShift GitOps. This allows development teams to:
-
Code, build, test, and debug directly from their browser, mirroring production environments without requiring local setup.
-
Release more quickly and test features, also enabling automated testing for earlier bug detection and improved Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR). Customers can also integrate existing CI/CD solutions into Red Hat Developer Hub.
-
-
It also complements Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes (ACS), which enforces security policies for containerized applications, ensuring only trusted artifacts run in the cluster.
The architecture aims to empower platform teams to define and curate trusted environments and tools, which developers then consume for accelerated, secure application delivery from development to production.
Typical RHADS deployment
RHADS is designed with a modular approach that allows it to be integrated seamlessly with a variety of supported tools and existing platforms and systems, including those already in use by customers. The following diagram shows a typical RHADS deployment, the components involved, and how they interact with each other. There are many icons, most of which are 3rd-party products already in use by customers, demonstrating the flexibility and extensibility of RHADS.
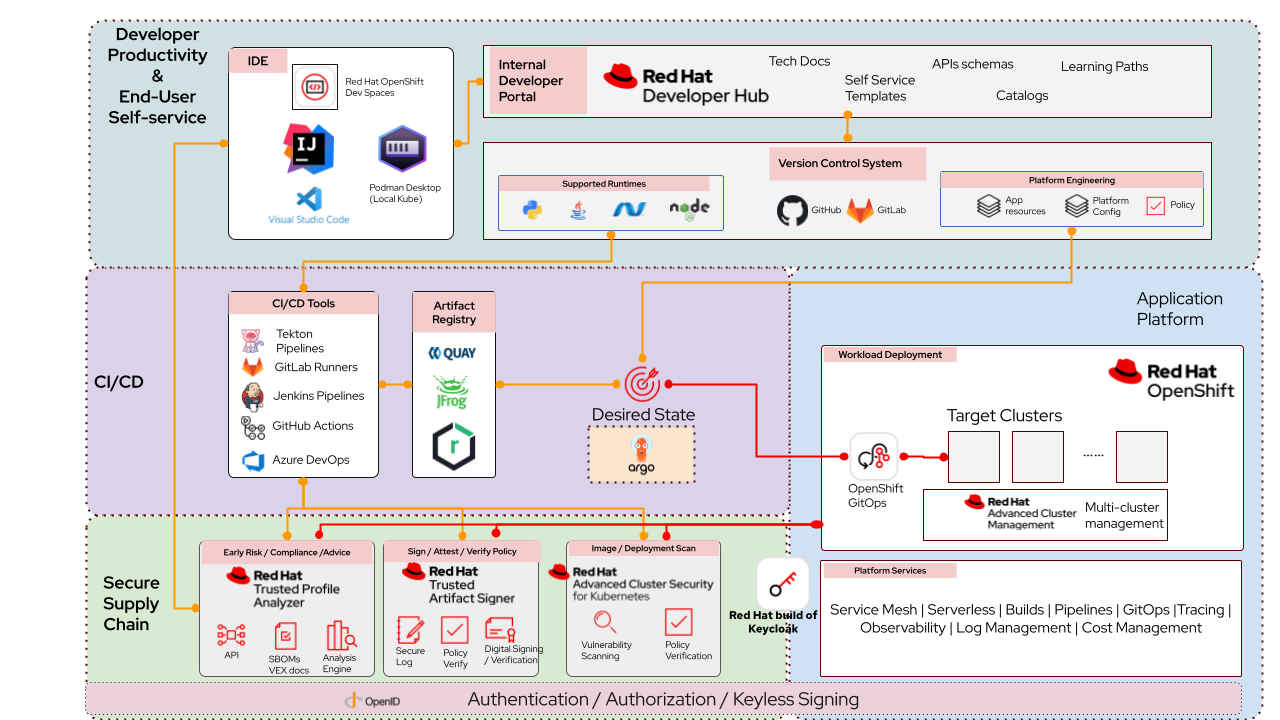
Here is a summary of the components and their roles based on the diagram above.
Developer Productivity & End-User Self-Service
IDE (Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces, IntelliJ, VS Code, Podman Desktop)
Provides cloud-native development environments, enabling developers to code using familiar tools. These IDEs integrate with the Developer Portal and CI pipelines, allowing seamless transition from code to build. Podman Desktop is a lightweight, rootless, and Docker-compatible desktop GUI tool designed for developers to manage containers and Kubernetes locally, facilitating consistent development environments, experimentation with AI models via its AI Lab extension, and seamless integration with OpenShift.
Internal Developer Portal (Red Hat Developer Hub)
A centralized hub offering self-service templates, API documentation, component catalogs, and learning paths for developers. It also provides plugins to integrate with other tools and services including Red Hat OpenShift and a variety of 3rd party components. It connects developers with resources and tools across the development lifecycle, and enables team collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Continuous Integration & Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD Tools (Tekton, GitLab Runners, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, etc.)
Automates building, testing, and integration of code changes. It pulls source code from version control and produces deployable artifacts. It also integrates with RHTAS to sign artifacts. RHADS is flexible enough to allow customers with other leading CI/CD solutions, such as Jenkins pipelines and GitHub Actions, to integrate them into Red Hat Developer Hub. This ensures that customers can continue to leverage their existing CI/CD investments.
Secure Supply Chain
Early Risk/Compliance Analysis (Red Hat Trusted Profile Analyzer)
Analyzes Software Bills of Materials (SBOMs) and VEX documents to detect vulnerabilities early in the development cycle. Integrates with CI pipelines to inform developers of potential risks. It also integrates with OpenShift Dev Spaces to provide a unified view of the application’s security posture directly from the IDE.
Application Platform
GitOps (OpenShift GitOps)
Automates application deployment and lifecycle management using Git repositories (the "Desired State") as the source of truth. Applies the desired state to clusters and continuously reconciles the actual on-cluster state with the desired state to maintain consistency.
Cross-Cutting Concerns
Authentication / Authorization / Signing
Uses OpenID Connect providers like Red Hat build of Keycloak for secure identity and access management. Digital signing ensures trust across all pipeline stages. RHADS supports both keyless and key-based signing, using existing user identities like GitHub, Google, or SSO, and maintains an immutable audit trail for maximum transparency and trust.
RHADS Install Options
RHADS is designed as an add-on offering for Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus. Additionally, using Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer to sign/verify artifacts and Red Hat Trusted Profile Analyzer to analyze software profiles on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is supported.
-
Deployment Locations: RHADS components can be deployed wherever OpenShift is deployed, including on Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) and Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA). Crucially, RHADS can also be deployed on non-OpenShift Kubernetes platforms.
-
Managed Offering: It is not available as a managed offering; RHADS components are self-managed by the customer.
-
Bare Metal: RHADS can be sold on bare metal OpenShift clusters exclusively. For non-OpenShift clusters on bare metal, per-core and per-user options should be used.
RHADS component installation options
RHADS components and the complementary developer tools can be installed in a variety of ways to support local, disconnected, and cloud environments.
| Deployment Type | Features and Capabilities |
|---|---|
Local (Developer Desktop) Install |
|
Disconnected/Air-Gapped Environment deployments |
|
Self-Managed OpenShift and Managed OpenShift Cloud Services deployments |
|
In essence, RHADS provides a robust framework that supports developers whether they prefer cloud-based environments, local container development, or integrated IDE experiences, all while embedding security and streamlining workflows.