Introduction to AI for AI Engineers
|
Quick Logout Links Prior to starting this module, click the following two links and make sure you log out of previous sessions to prevent errors related to performing actions as the wrong user. |
Introduction
In this module, you will review AI concepts for Engineers, including frameworks, protocols, and tools to build AI applications.
Study Case
In this module, you have the opportunity to explore a role with a fictional company. You are a Consultant working for a global bank called ACME, with many branches worldwide. Your role is to introduce AI capabilities to the bank, ensuring its adoption including best practices, security, and standardization. Before making recommendations or choosing an approach, you must learn critical concepts for building AI applications.
AI Overview
The rise of AI has created new roles in the industry, such as AI Engineers. These personas are responsible for building AI solutions, such as a chatbot, AI assistants, fraud detection systems, AI Agents, and more. The challenge is to bring standardization in a consistent, secure, and transparent way to drive adoption of AI.
The diagram below shows the key personas involved in the AI development lifecycle and how they interact. Understanding these roles will help you achieve your goal as a Consultant since it will help you engage with the appropriate teams and make recommendations for future projects.
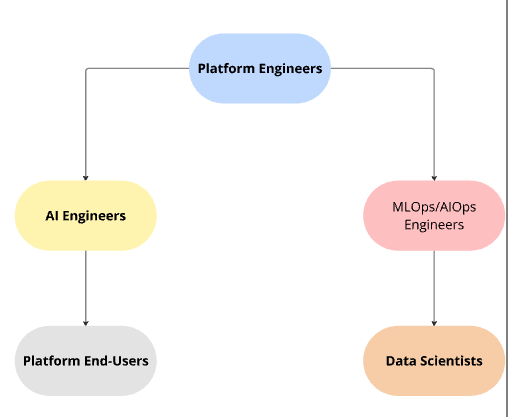
Platform Engineers build and maintain ACME’s Application PLatform: OpenShift. An application platform that provides foundational technologies with the necessary tools to support MLOps and AIOps engineers efficiently deploy models to production while following best practices. Then, AI Engineers will build AI applications using the deployed large language models (LLMs) that the Data Scientists first trained and built.
In the next sections, you will explore core AI concepts around AI applications, including standards, frameworks and protocols.
Overview of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Organizations seek to integrate AI into their software ecosystems to drive business value. To achieve this, AI applications must be capable of understanding technical concepts specific to their industry and organization.
Foundational models are enhanced using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques to improve the LLM’s output with domain-specific business knowledge, such as information about bank-specific products or customer loyalty programs.
A potential use case is a RAG-enabled chatbot that can query information related to ACME bank’s products and services. This enables the chatbot to provide customers with product and services information when they are looking to open a bank account or explore additional financial products.
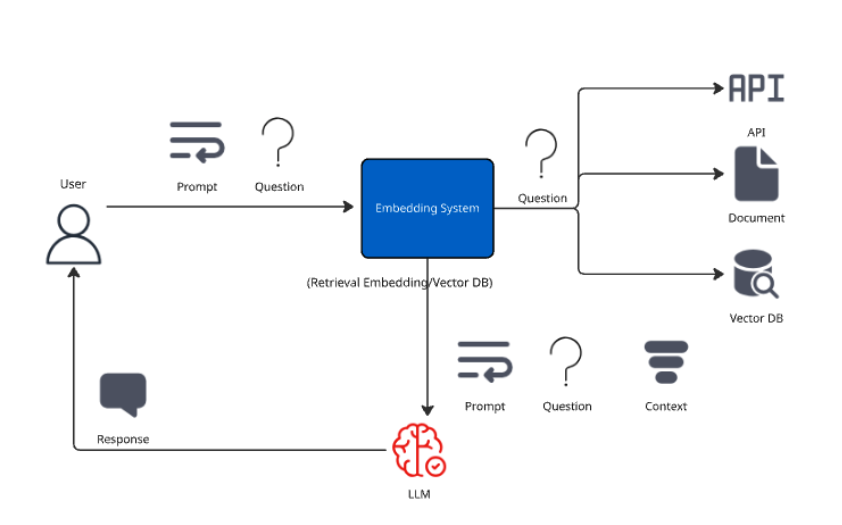
How does RAG work?
-
Data Collection: Data is collected from both structured (databases) and unstructured data (documents, marketing materials, blogs). This process can be accomplished asynchronously to keep the system up to date with the latest sources. Think of this as an ETL process, but with a specialized step to convert data into a format the LLM can query.
-
Embedding system: Once the user submits a question, an intermediary system converts it into a numerical representation (embedding) - this allows it to be compared to the existing data.
-
Retrieval: The system compares the resulting embedding against the data sources looking for similarities in content.
-
Augmentation: This retrieved context and the question will be creating an augmented prompt to be sent to the LLM for processing.
-
Generation: The LLM will generate a response for the user.
Benefits
-
Up-to-date Information: RAG techniques enable LLMs to keep information updated with relevant sources.
-
Reduced Hallucinations: RAG reduces hallucinations given the specific domain knowledge acquired from the different sources.
-
Enhanced Domain-Specific Knowledge: With RAG, organizations can customize the LLM with specific knowledge according to their business needs and goals.
-
Transparency: Organizations control the model-specific knowledge domain based on the sources used during RAG.
AI Agents
Agents are applications that, on behalf of the user and autonomously, execute actions according to specific prompts using LLMs and third-party tools such as websites, databases, and APIs.
AI Agents vs AI workflows
An AI workflow is a predefined series of steps to accomplish several tasks with one or many goals, including AI for logic or decision making based on previous information or specific parameters.
Agents can make decisions and use reasoning to achieve a specific outcome without a clear path. So, Agents do not need the predefined steps or sequences a workflow needs and can therefore solve varying cases.
For example, an AI workflow could be deciding if bank customers should be managed by different services/departments based on certain information, credit check, salary range, etc. An AI agent could determine if a customer should receive a loan and how much based on different information such as customer profile, customer annual spent, credit background, and customer financial profile. The AI agent can process complex information and make decisions accordingly.
Agent Frameworks
AI Agent Frameworks help developers to build AI agents by reducing boilerplate code, standardizing building blocks to be reused during agent implementation.
Agent Protocols
Agent2Agent (A2A)
Agent2Agent is an open protocol designed to manage the communication between agents, providing standard synchronous communication with JSON-RPC 2.0 and asynchronous push notifications. The protocol supports standard security protocols, and enables agent discovery using Agent Cards to access detailed information about a available agents.
This is one of the most well-known agent protocols within their respective domains. While there are other competing protocols, these represent the current leading standards. Red Hat is not backing a specific protocol, but watching the market and will continually evaluate each protocol for market efficacy.
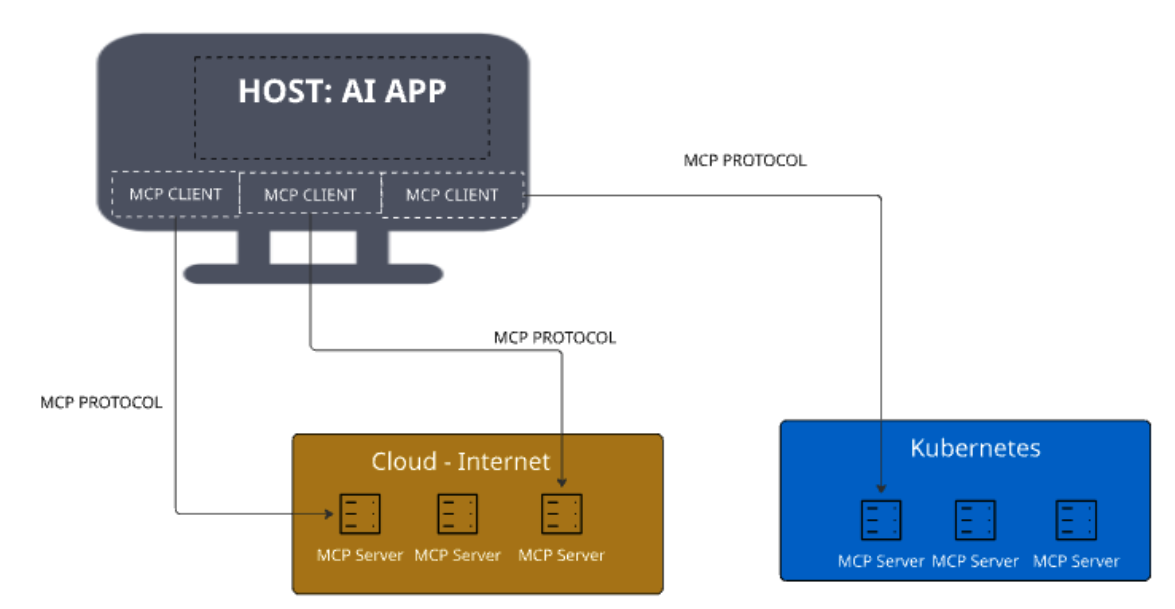
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol is an open protocol, created by Anthropic. It provides a standardized way for AI agents to expose and interact with tools and data sources, making it easier to build AI agents, workflows, and applications. It defines how applications can call external tools, retrieve data, and interact with other systems to enhance their capabilities. MCP provides defines both MCP clients and MCP servers. Developers can use MCP servers to enhance their applications by building functionalities that later will serve MCP clients that any AI applications will consume.
Llama Stack Overview
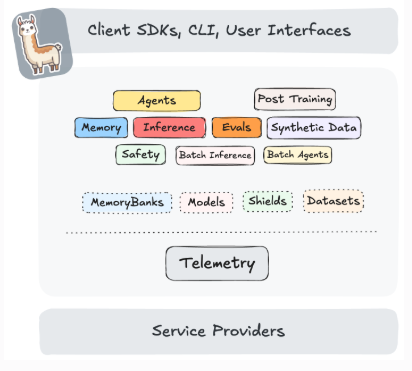
To standardize and bring best practices. Llama Stack (an open-source framework developed by Meta) consists of a set of tools for creating generative AI applications using standardized APIs.
The following image, created by the Llama Stack community, shows the key components of Llama Stack are:
-
Unified API layer supporting:
-
Plugin architecture that supports many APIs across various environments (mobile, cloud, on-premise). This architecture allows for rapid deployment of prepackaged and verified distributions.
-
Developer interfaces, including a CLI and SDKs for Python, Node.js, iOS, and Android.
-
Agents
-
Eval
-
Inference
-
RAG
-
Safety
-
Telemetry
-
Tools
-