Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite Enablement L3 RHEL
Welcome to the Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite Enablement (RHADS) workshop on RHEL. This workshop provides hands-on experience with two critical Red Hat security solutions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments that are included in RHADS: Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer (RHTAS) and Red Hat Trusted Profile Analyzer (RHTPA). Unlike Red Hat Developer Hub, RHTAS and RHTPA are fully supported on RHEL.
Use Cases
Use of RHTAS and RHTPA on RHEL is generally used when:
-
You wish to ensure the integrity and authenticity of your software artifacts in a pure RHEL environment.
-
You primarily use non-RHEL or non-OpenShift environments (e.g. xKS) for development and production, but you wish to use RHADS security components (RHTAS and RHTPA) on a supported environment (RHEL)to secure your software supply chain.
RHEL vs. OpenShift
-
On RHEL, you generally install TAS and TPA "directly" (e.g. via Ansible, system services, configuring components) as a more “traditional” server deployment.
-
On OpenShift, TAS and TPA are deployed via an Operator / Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) model, leveraging the Kubernetes-style control plane for lifecycle, scaling, multi-tenancy, and orchestration.
-
Thus, many operational concerns (scaling, upgrades, dependency wiring, multi-pod management, certificate handling, service routing) are handled differently (and more declaratively) in the OpenShift setup.
On RHEL, TAS and TPA are deployed as podman pods (so some concepts from Kubernetes like Deployments, ConfigMaps, etc apply), and are configured as system services (via systemd) that are managed through traditional RHEL administration tools and processes, including security (firewall, SELinux, etc.) and networking (firewall, routing, etc.). You can use the provided Ansible playbooks to do administrative tasks like backup/restore, key rotation, and more.
Benefits of RHTAS and RHTPA on RHEL
-
Full control over installation and configuration (manual or Ansible-driven).
-
Can run on bare metal or virtual machines without needing a Kubernetes/OpenShift cluster.
-
Lighter footprint — no cluster orchestration overhead.
-
Easier to integrate into traditional infrastructure environments.
-
Flexible for custom setups (networking, databases, identity providers).
-
Good for smaller deployments or environments without container platforms.
For more information on RHTAS and RHTPA, consult the enablement courses for these solutions on OpenShift as part of the wider RHADS enablement series.
Workshop Overview
This workshop consists of two comprehensive modules designed to help you understand, install, and configure Red Hat’s advanced security solutions on RHEL:
Workshop Environment
This workshop environment is pre-configured with:
-
Red Hat Build of Keycloak (acting as an OpenID Connect provider)
-
A pre-installed Ansible Execution Environment (EE) container image with the required Ansible Collections for the products (these can also be downloaded separately and used with a custom execution environment of your own)
The workshop uses a multi-machine architecture where Ansible jobs run from a bastion server to deploy and configure the security components:
-
Bastion Server: (hostname:
bastion) Includes Ansible developer tools and executes playbooks to install and configure TAS and TPA on target machines -
TAS Machine: (hostname:
rhtas) Dedicated RHEL 10 machine where Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer is installed and configured -
TPA Machine: (hostname:
rhtpa) Dedicated RHEL 10 machine where Red Hat Trusted Profile Analyzer is installed and configured -
Utility Machine: (hostname:
utility) Contains Red Hat Build of Keycloak pre-installed and pre-configured as an OpenID Connect provider for authentication and authorization across all components. It also includes vanilla instances of PostgreSQL for use by Keycloak, RHTAS and RHTPA.
To check out the Keycloak configuration, navigate to the Keycloak admin console and login with the following credentials:
-
Username:
{rhbk_admin_username} -
Password:
{rhbk_admin_password}
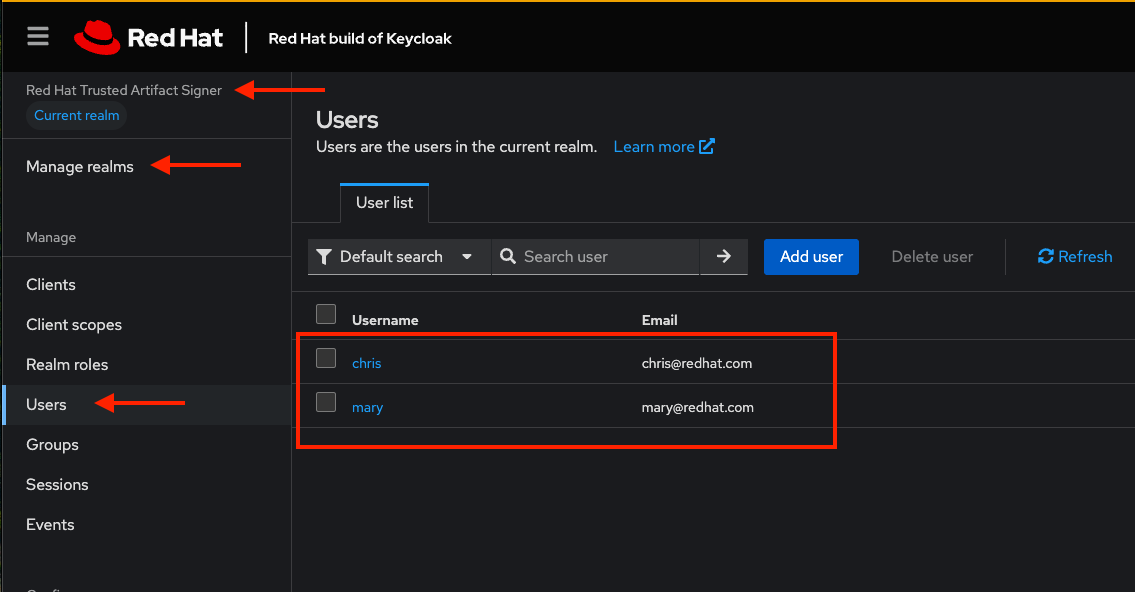
Keycloak has been pre-configured with the trusted-artifact-signer realm (used for TAS) and chicken realm (used for TPA). By clicking on Manage Realms you can switch between the two realms, and click on Users to view the predefined users in each realm (these realms, clients, and users will be used in the exercises). Feel free to explore the other sections of the Keycloak admin console, but try not to change anything until after you have completed the exercises!
Prerequisites
Before starting these exercises for RHEL, ensure you have:
-
A modern web browser
-
Basic knowledge of Linux command line operations
-
One of the following
registry.redhat.iocredentials:-
A Red Hat account with username/password.
-
A Red Hat Registry Service Account with username/token (which you will use as your password).
-
|
If you do not have registry credentials, please visit the Registry Authentication article on the Red Hat Customer Portal and create an account and remember your username and password. You can also create a new or use an existing Registry Service Account and remember your username and token. |
Lab Environment
Both terminal windows to your right are already logged into the lab environment as the lab-user user via ssh.
You will use these terminal windows to complete most steps of this workshop. Both are identical, but keep in mind that environment variables defined in one terminal will not be available in the other unless you explicitly set them in the other terminal.
Each module is self-contained and can be completed independently, allowing you to focus on the solutions most relevant to your needs.