Configure the GitLab Integration
|
Red Hat Developer Hub can integrate with various source control solutions. A self-hosted instance of GitLab is used in this coursework to ensure stability and accuracy of the content, since managed solutions are subject to changes outside of our control. |
The GitLab plugin enables Red Hat Developer Hub to integrate with GitLab to enable the following functionality:
-
Discover and import
catalog-info.yamlfiles from GitLab repositories. -
Enable Software Templates to create new repositories and automate opening pull/merge requests.
-
Display open issues, merge requests, scorecards, and CI status directly in Red Hat Developer Hub.
Configuring the integration requires:
-
Generating an access token in GitLab.
-
Creating a Secret to store the access token, and loading it into the Red Hat Developer Hub pod.
-
Adding the access token and GitLab hostname to the
integrationssection of Red Hat Developer Hub’s app-config.yaml. -
Registering a new
gitlabprovider incatalog.providersin the app-config.yaml.
Create the GitLab Token and Credentials Secret
Create the GitLab Token
To facilitate secure communication between Red Hat Developer Hub and the GitLab API, you need to generate an access token:
-
Visit the GitLab instance deployed in your environment.
You can find the GitLab instance deployment by accessing the {openshift_console_url}[OpenShift Web Console] and viewing the
gitlabproject. Do not edit or delete anything in this project! -
Login using the root credentials:
-
Username:
root -
Password: {gitlab_user_password}
-
-
Click on your user’s profile picture, select Edit profile, then Access tokens.
-
Click the Add new token button, then set the following values for the token:
-
Token name:
developer-hub-integration -
Scopes:
api,read_repository,write_repository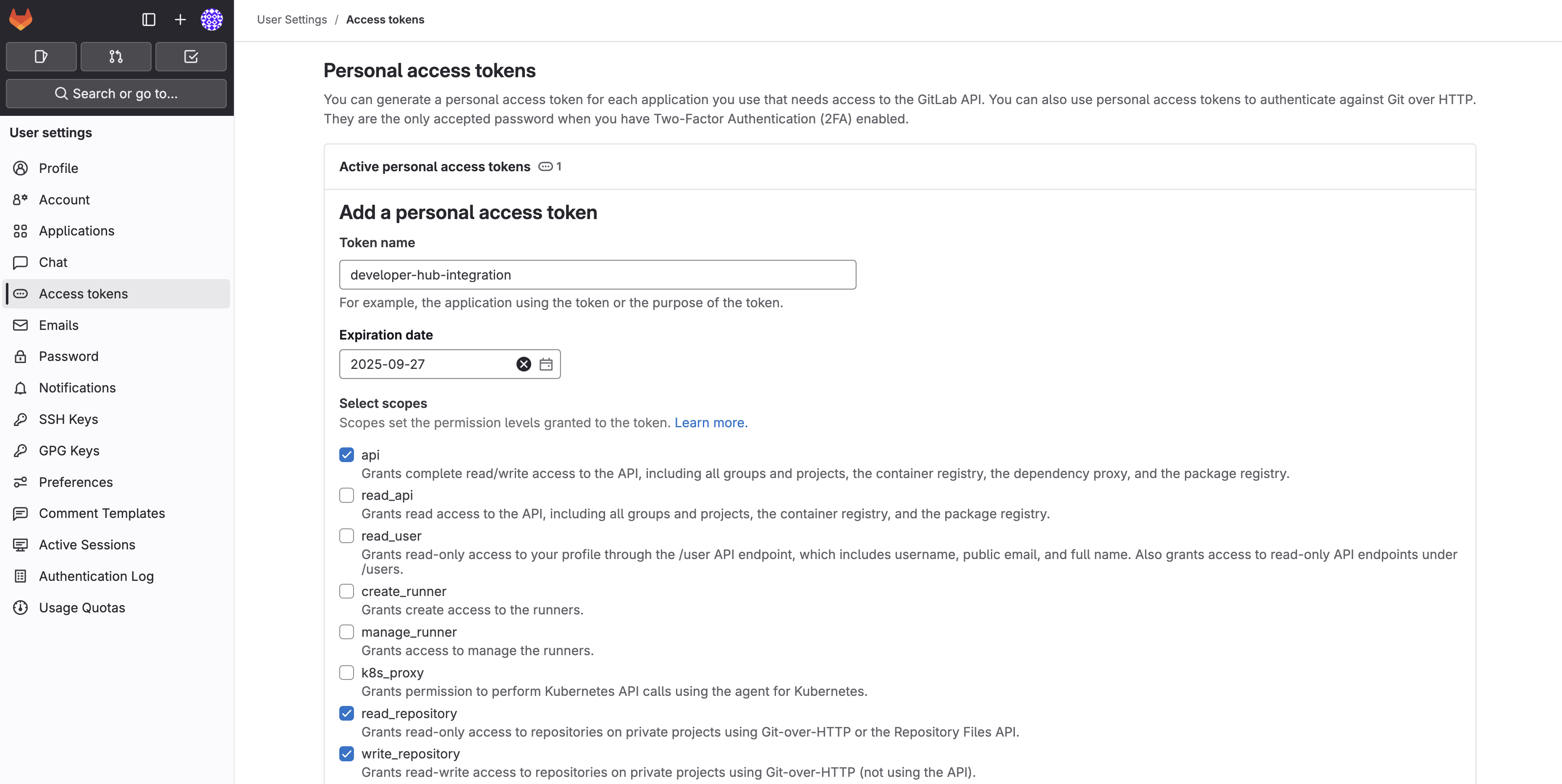
-
-
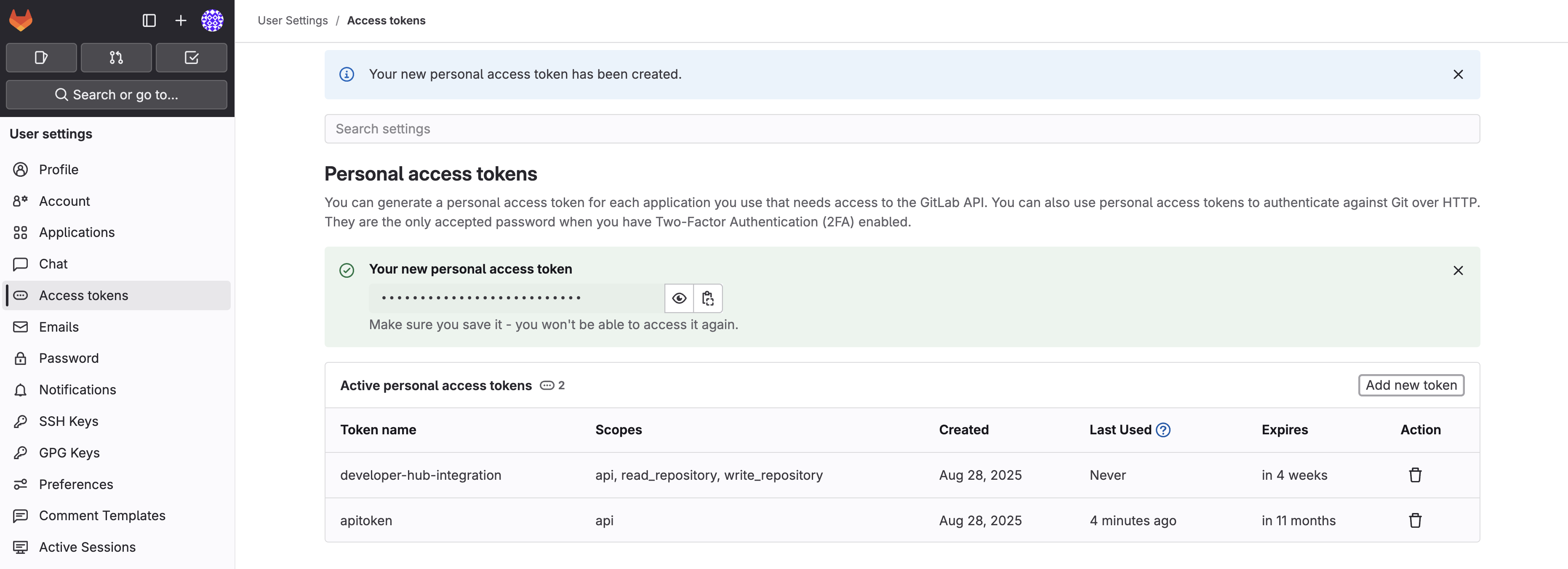
Scroll down and click Create personal access token.
-
Once the token is created, copy it someplace safe - you’ll need it in the next section.
Create the GitLab Secret
Create a Secret to store the GitLab token and hostname:
-
Log in to the {openshift_console_url}[OpenShift Web Console] using the following credentials:
-
Username:
{openshift_admin_user} -
Password:
{openshift_admin_password}
-
-
Navigate to Workloads > Secrets and click Create > From YAML.
-
Ensure that the
setup-rhdhproject is selected. -
Replace the content in the YAML editor with the following:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: gitlab-secrets namespace: setup-rhdh type: Opaque stringData: GITLAB_HOST: gitlab-gitlab.{openshift_cluster_ingress_domain} GITLAB_TOKEN: YOUR_TOKENMake sure to replace the
YOUR_TOKENplaceholder with the token you generated in GitLab. -
Click Create.
Similar to the keycloak-secrets you created in the previous section, you need to tell Red Hat Developer Hub to actually read the new Secret.
Update the Red Hat Developer Hub Configuration
Add GitLab Secrets to the Backstage CR
Update your Backstage CR to include the GitLab secret:
-
Navigate to your Backstage CR in the OpenShift Web Console and change to the YAML view.
-
Update the
extraEnvs.secretssection to reference the gitlab-secrets Secret you created:extraEnvs: secrets: - name: keycloak-secrets # Inject the GITLAB_HOST and GITLAB_TOKEN into # the pod as environment variables - name: gitlab-secrets -
Click Save.
Add the GitLab Dynamic Plugin
Enable the GitLab plugin by updating your dynamic-plugins-rhdh ConfigMap:
-
Navigate to Workloads > ConfigMaps and click on
dynamic-plugins-rhdh. -
Click Edit ConfigMap.
-
Update the
dynamic-plugins.yamlcontent to include GitLab catalog backend plugin:- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-plugin-catalog-backend-module-gitlab-dynamic disabled: falseVerify that your indentation is correct by aligning it with the existing Keycloak plugin.
-
Click Save.
Update Backstage Configuration to Enable GitLab Integration
Update your app-config.yaml to include GitLab integration and provider configurations:
-
Navigate to Workloads > ConfigMaps and click on
rhdh-config. -
Click Edit ConfigMap.
-
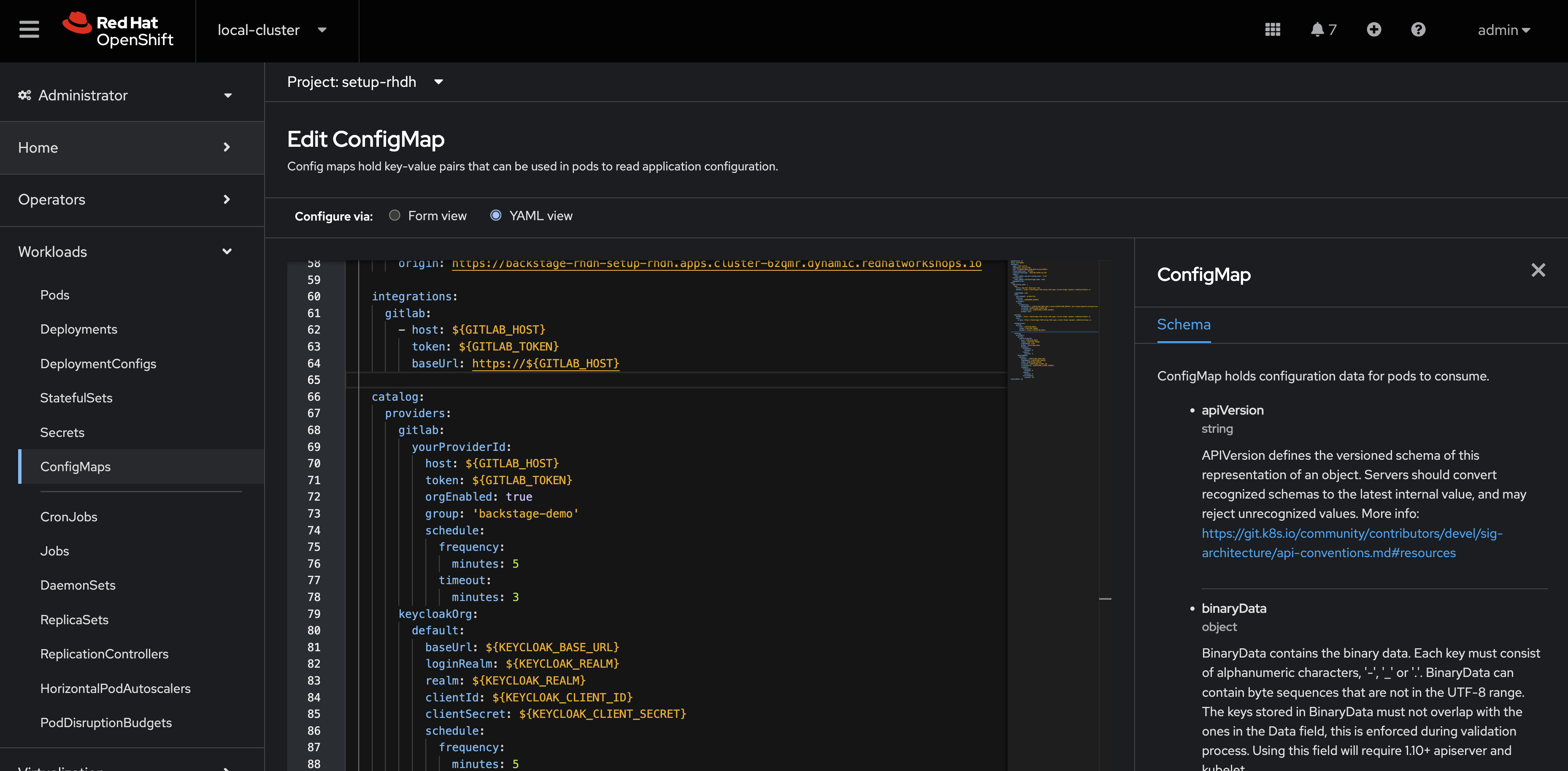
Add the following
gitlabconfiguration to thecatalog.providerssection of your app-config.yaml:catalog: providers: # ...existing providers, e.g keycloak # ................................... # Our new GitLab provider that will synchronize catalog-info.yaml # from our repositories in GitLab to the Software Catalog gitlab: yourProviderId: host: ${GITLAB_HOST} orgEnabled: true group: rhdh # Normally the entity filename is just set to catalog-info.yaml # In this case we're hardcoding a path to a specific example file entityFilename: discovery-example/catalog-info.yaml schedule: frequency: minutes: 5 timeout: minutes: 3 -
Additionally, add a new
integrationssection at the root level of the app-config.yaml, i.e. the same indentation level as thecatalogandappkeys:integrations: gitlab: - host: ${GITLAB_HOST} baseUrl: https://${GITLAB_HOST} apiBaseUrl: https://${GITLAB_HOST}/api/v4 token: ${GITLAB_TOKEN} -
The resulting configuration should resemble this screenshot.
-
Click Save to update the app-config.yaml.
Verify GitLab Integration
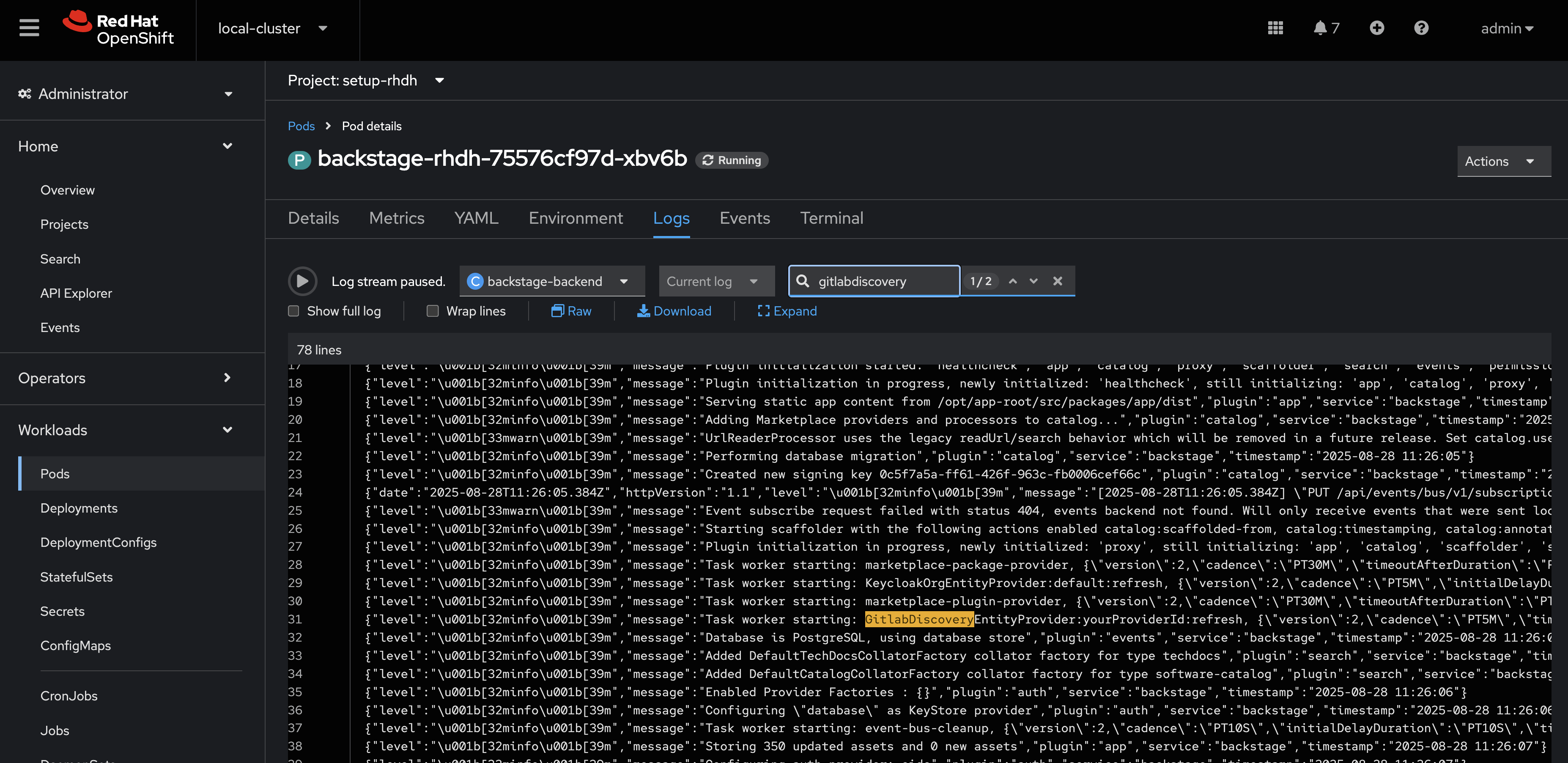
After the new Backstage pod has started:
-
Check the Backstage pod logs to confirm successful synchronization with GitLab.
-
Next, log in to your Red Hat Developer Hub instance.
-
Navigate to the Catalog to see imported items of Kind Component from GitLab repositories - specifically a HTTP Sink Application.
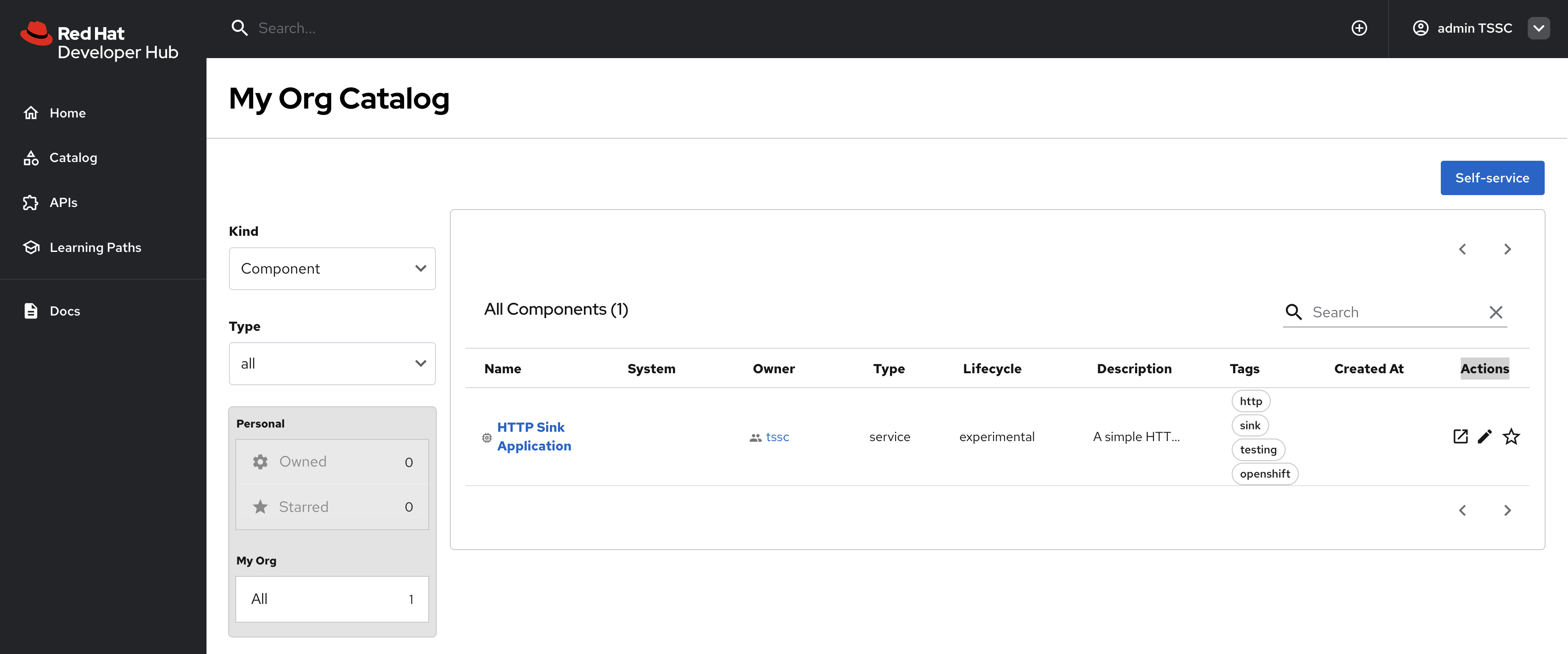
-
Visit the APIs screen using the link in the side menu and you’ll find a matching API Entity. Click it.
-
A Relations pane shows that the API is provided by the HTTP Sink Application.
-
Click the Definition tab - an Swagger UI is rendered from the OpenAPI Spec.
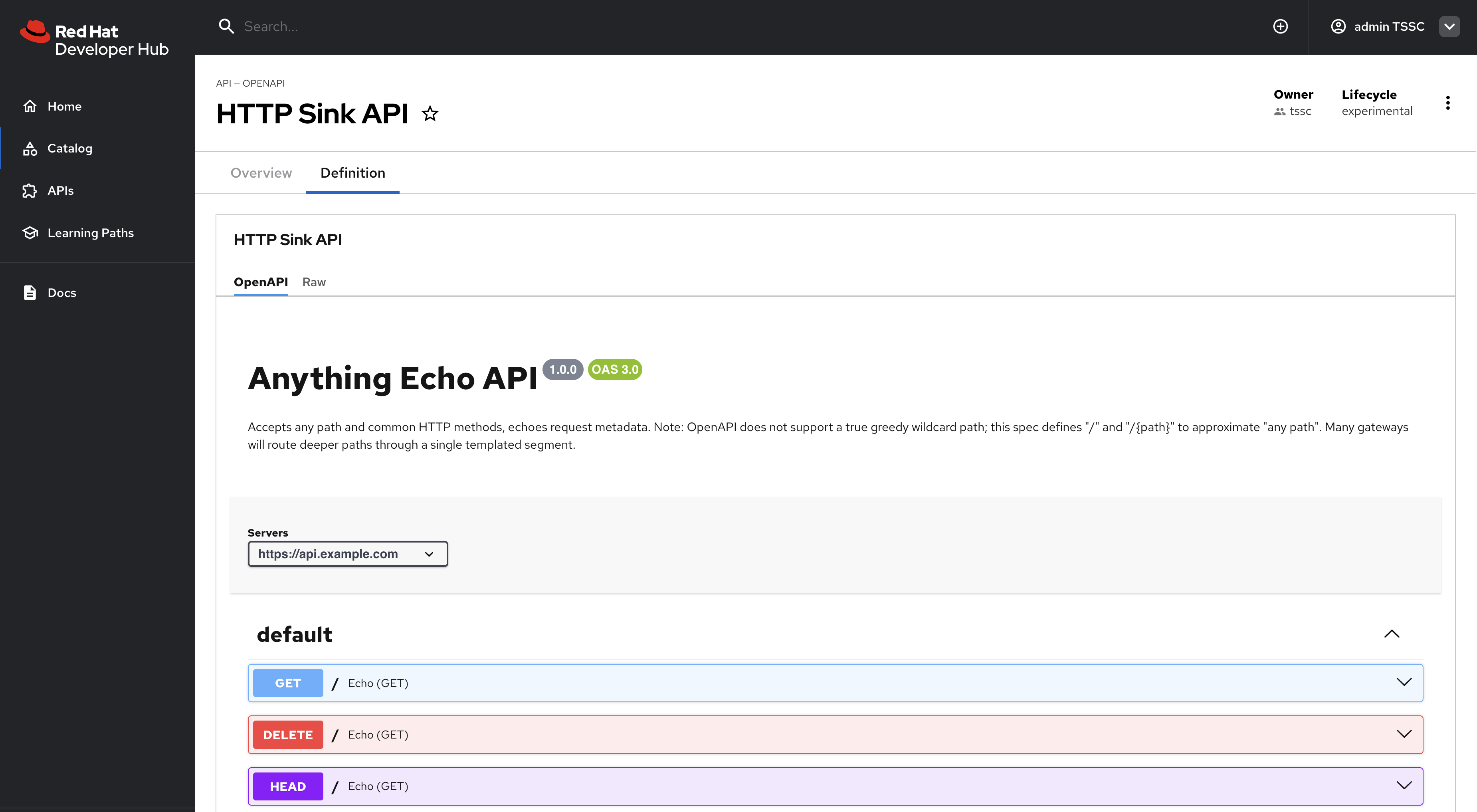
-
Return to the Overview tab and click View Source. You’ll see the catalog-info.yaml and opeanapi.yaml that the GitLab plugin discovered to generate these entities.
The system automatically discovers and imports catalog-info.yaml files from repositories in the configured GitLab group, so long as they match the specified search parameters.
|
The GitLab integration will scan the specified group ( |